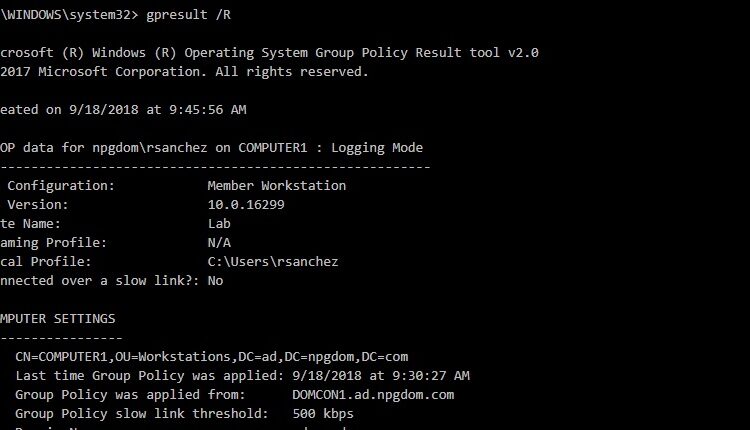
Group Policy is the easiest way to reach and configure settings for computers and users on Active Directory (AD DS) based networks. Group Policy is applied either on the computer settings (when windows starts), or on the user settings (after the user has logged on to the computer) or on both simultaneously and their configurations apply to objects like site (when the configuration acts on the whole site), domain or organizational units. So how to force gp updates? Here are the options for you.
The Right Configuration for You
The computer configuration makes it possible, for example, to install software as soon as the computer starts up, to make scripts when the computer starts up, to deploy Windows updates on client workstations, to define password policies, modify computer security settings, deploy wallpaper images, deploy remote desktop services, prevent a program or script from running on a computer, define groups restricted.
- The user configuration makes it possible to install software from the opening of the session, to deploy start-up scripts, to deploy the software on the workstations, to prohibit the use of an application by a user.
The requirements for using group policies should be based on:
The AD DS-based network: installing the AD DS role on one of the servers
The workstations that must be a member of the domain and the users that must use the domain credentials to log on.
Permission to have the ability to modify group policies or be the system administrator
Opening the Group Policy Object Editor console can be done either using the command line, the Microsoft Management Console (MMC) tool, or the Group Policy Management Console.
- From the command line: Click on the Start button, then in the search box type gpedit.msc and press the Enter key.
- From the Microsoft Management Console tool: Click on Start, click in the Search box, type mmc, then press Enter. On the File menu, click Add / Remove Snap-in. In the latter’s dialog box, click on Group Policy Object Editor, then on Add.
- From the Group Policy Management Console: click on Tool, then on Group Policy Management. Right click on a group policy name, then click Modify.
To create a new Group Policy Object, in the Group Policy Management console, you must:
Right-click on an organizational unit, right-click and click on “Create a GPO object in this domain and link it here”, type in the name of the GPO and validate. The GPO will be directly linked to this organizational unit.
- Either right-click on the “Group Policy Objects” folder, click on New, type in the name of the GPO and validate. It will then be necessary to assign this GPO to an organizational unit that will use it. To do this, you must select an organizational unit and click on “Link an existing Group Policy Object”, select the GPO you want to link and validate.
AppLocker is a new feature in Windows that allows you to specify users or organizational groups to run applications based on the unique identity of files, and replace the software restriction policies feature of previous versions of Windows. With AppLocker, it is possible to create rules to allow or deny the execution of applications and to respond to a number of challenges and constraints in terms of application execution control, which applications a user can run, protection against unauthorized software and license compliance.